This is a practice of Langgraph agent, which is used to interact with a sqlite database. It is referring to Langgraph tutorial sql-agent, with replacing the LLM by Tongyi Qwen. This article is used to document the learning during the practice.
本文是对于Langgraph中agent的一次实践,是用来与Sqlite数据库进行交互。本文参照了Langgraph的教程,仅使用通义千问替换了其中的LLM模型。本文用来记录实践过程中的学习心得。
Source code is uploaded here and would possibly be updated with time being.
源代码已上传,可能会不定期更新。
Overall Architecture
The overall architecture is depicted as following image. It is a combination of multiple tools and LLM invocations. It is designed to provide robust support to natural language query to RDBMS.
下图是该Agent的整体结构。该结构整合了多个工具和LLM模型的使用,用以提供自然语言进行RDBMS查询的有力支持。
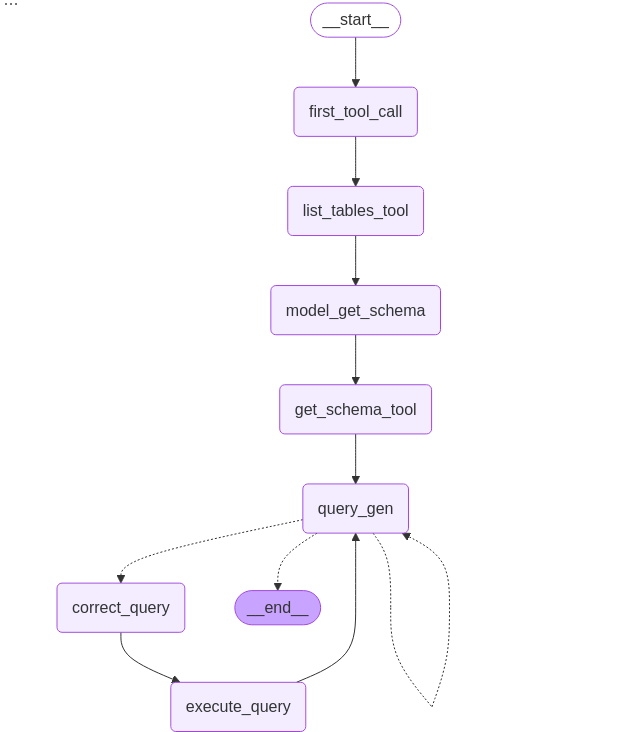
The responsibility of each node is described in following table:
其中的每个节点的功能概括见下图:
| Node | Next | Function | Use LLM | LLM Tool |
| first_tool_call | Fix: list_table_tool | first_tool_call | No | |
| list_tables_tool | Fix: model_get_schema | list_tables_tool(sql_db_list_tables) | No | |
| model_get_schema | Fix: get_schema_tool | Yes | get_schema_tool | |
| get_schema_tool | Fix: query_gen | get_schema_tool | No | |
| query_gen | Condition: correct_query Condition: END | query_gen_node | Yes | SubmitFinalAnswer |
| correct_query | Fix: execute_query | model_check_query | Yes | db_query_tool |
| execute_query | Fix: query_gen | db_query_tool | No | |
| END |
Detail Explanation
Following section is detail explanation of each step.
接下来是对每一部分的详细解读。
Node 1: first_tool_node
该节点使用了同名工具函数first_tool_call。首先定义函数first_tool_call。
# 定义工具函数first_tool_call
def first_tool_call(state: State) -> dict[str, list[AIMessage]]:
return {
"messages": [
AIMessage(
content="",
tool_calls=[
{
"name": "sql_db_list_tables",
"args": {},
"id": "tool_abcd123",
}
],
)
]
}
# 绑定工具函数到节点
workflow.add_node("first_tool_call", first_tool_call)可以看到,该函数固定直接返回了一个Message字典,是hardcode处理的。如果要进行抽象化处理,可以认为LLM经过决策,发现首先需要列举出数据库中的所有表对象,那么需要进行一个工具调用,sql_db_list_tables就是合适的工具。因此,该节点返回了决策结果,AIMessage中包含了工具名称,调用需要的参数(sql_db_list_tables不需要输入参数,所以args是空的),以及唯一的id。
Node 2: list_tables_tool
该节点依赖同名工具函数list_tables_tool,不过在其基础上包裹了一层异常处理。
首先看一下包裹的异常处理函数create_tool_node_with_fallback:
def create_tool_node_with_fallback(tools: list) -> RunnableWithFallbacks[Any, dict]:
"""
Create a ToolNode with a fallback to handle errors and surface them to the agent.
"""
return ToolNode(tools).with_fallbacks(
[RunnableLambda(handle_tool_error)], exception_key="error"
)
def handle_tool_error(state) -> dict:
error = state.get("error")
tool_calls = state["messages"][-1].tool_calls
return {
"messages": [
ToolMessage(
content=f"Error: {repr(error)}\n please fix your mistakes.",
tool_call_id=tc["id"],
)
for tc in tool_calls
]
}该函数指定了异常发生的情况,通过fallback处理,调用handle_tool_error来返回一个ToolMessage,其中包含了异常提示,从而防止整个workflow陷入异常种植。
接下来定义工具函数list_tables_tool的定义:
from langchain_community.agent_toolkits import SQLDatabaseToolkit
toolkit = SQLDatabaseToolkit(db=db, llm=llm_chat_tongyi)
tools = toolkit.get_tools()
list_tables_tool = next(tool for tool in tools if tool.name == "sql_db_list_tables")这个定义看起来比较简单,使用到了Langchain的SQLDatabaseToolkit工具中预定义的sql_db_list_tables。然后workflow将这个工具包裹了异常处理之后,绑定给了该节点。
# Add nodes for the first two tools
workflow.add_node(
"list_tables_tool", create_tool_node_with_fallback([list_tables_tool])
)需要注意的是,这一步只是将工具绑定到节点上,并不代表工具一定会被执行。Langsmith测试结果提示,实际尝试执行的工具,是取决于前一步的AIMessage中指定的tool_calls中的工具名。
如果前一步指定的工具名在这一步没有绑定的话,这里会抛出类似”Error: sql_db_list_tables123 is not a valid tool, try one of [sql_db_list_tables].”的错误。
Node 3: model_get_schema
这一步使用到了LLM的能力,结合用户的输入,从所有的表对象中选取相关的表,并且按照工具sql_db_schema的要求生成调用参数。
首先,从SQLDatabaseToolkit工具集中引用了工具sql_db_schema。
get_schema_tool = next(tool for tool in tools if tool.name == "sql_db_schema")接下来,将该工具绑定给了LLM,并将LLM绑定给了当前节点。
# Add a node for a model to choose the relevant tables based on the question and available tables
model_get_schema = llm_chat_tongyi.bind_tools(
[get_schema_tool]
)
workflow.add_node(
"model_get_schema",
lambda state: {
"messages": [model_get_schema.invoke(state["messages"])],
},
)这样,model_get_schema这个节点就有了LLM的能力,并且它知道可以选用get_schema_tool这个工具。
实际执行的过程中,可以观察到针对这个LLM的调用,提示和生成结果分别是:
LLM 开始调用:
Prompts:
[
"Human: Which sales agent made the most in sales in 2009?\nAI: \nTool: Album, Artist, Customer, Employee, Genre, Invoice, InvoiceLine, MediaType, Playlist, PlaylistTrack, Track"
]LLM 调用结束:
"generations=[[ChatGeneration(generation_info={'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, message=AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_a2612321b7ba4cef894766', 'function': {'arguments': '{\"table_names\": \"Invoice, Employee\"}', 'name': 'sql_db_schema'}, 'type': 'function', 'index': 0}], 'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 23, 'prompt_tokens': 299, 'total_tokens': 322, 'completion_tokens_details': None, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': None, 'cached_tokens': 0}}, 'model_name': 'qwen-plus', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'id': 'chatcmpl-57b00381-d313-9e23-bf89-0f34a77b7624', 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-aa02fe70-a2aa-45a7-91e1-17c315da3c9b-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'sql_db_schema', 'args': {'table_names': 'Invoice, Employee'}, 'id': 'call_a2612321b7ba4cef894766', 'type': 'tool_call'}], usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 299, 'output_tokens': 23, 'total_tokens': 322, 'input_token_details': {'cache_read': 0}, 'output_token_details': {}}))]] llm_output={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 23, 'prompt_tokens': 299, 'total_tokens': 322, 'completion_tokens_details': None, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': None, 'cached_tokens': 0}}, 'model_name': 'qwen-plus', 'system_fingerprint': None, 'id': 'chatcmpl-57b00381-d313-9e23-bf89-0f34a77b7624'} run=None type='LLMResult'"该节点返回的信息中,可以看到finish_reason是tool_calls,表明模型给出了处理建议,是对工具的调用。具体的调用方式,是tool_calls=[{‘name’: ‘sql_db_schema’, ‘args’: {‘table_names’: ‘Invoice, Employee’}, ‘id’: ‘call_a2612321b7ba4cef894766’, ‘type’: ‘tool_call’}]。
在解读实际行为的时候,有一些思考和猜想,记录下来以供日后有机会进一步验证。
- 为什么LLM会产生这样的输出格式?基于对以上观察结果的理解,一个猜想是,Langchain/Langgraph框架对于模型的调用做了封装,在实际调用过程中,引导模型根据提示,生成了特定格式的输出。
- 为什么在输出中,可以得到调用工具的具体表达式?Langchain框架实现了对于工具函数的自动读取和解析。框架假定工具函数的函数说明,以及内部变量中的name, description, args_schema,包含了函数的功能描述和参数描述。通过将这些信息转化为格式化的信息,并提供给LLM阅读和理解,帮助LLM正确理解函数作用,并返回可以调用函数的表达式。
这一步实际上是借用了LLM的理解和判断能力,将非结构化的要求(用户自然语言输出),结合结构化的工具信息,生成了结构化工具调用表达式,为下一步实际执行提供输入。
Node 4: get_schema_tool
这一步非常直接,就是将同名工具get_schema_tool绑定给了get_schema_tool节点。
workflow.add_node(
"get_schema_tool",
create_tool_node_with_fallback([get_schema_tool])
)在前一个节点,我们通过LLM的判断,生成了tool_calls的具体执行表达式。在这一步,框架会寻找可以执行表达式的工具。我们在这里将工具绑定后,框架就会实际调用工具函数进行处理了。
下图的Langsmith的结果提示,这一步的Input中的最后一项是AIMessage,内容是前一步产生的调用表达式;而Output则是表结构检查的结果。
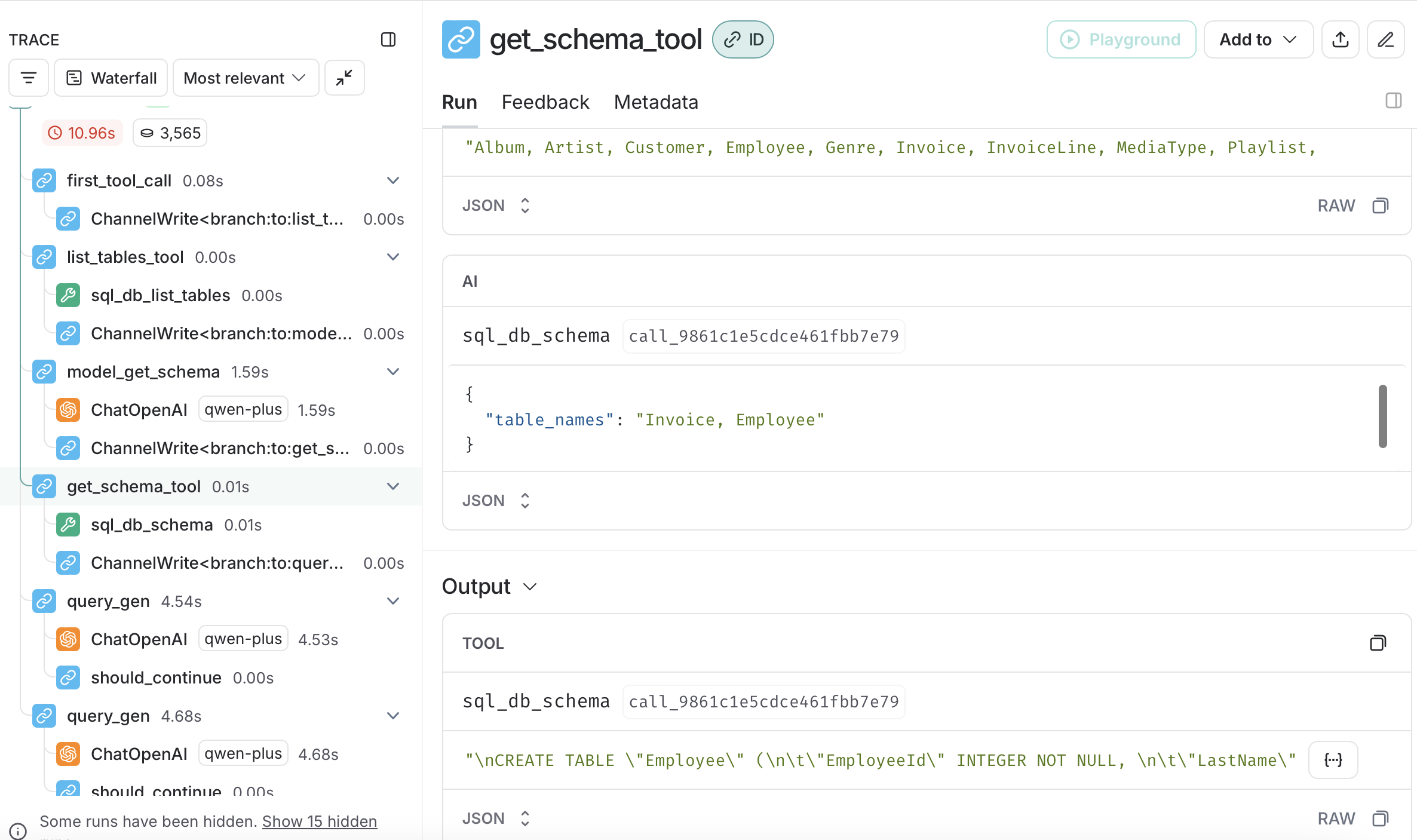
Node 5: query_gen
query_gen节点是这个工作流中最复杂的一个,主要体现在:
- 同样绑定了LLM
- 包含了决策路径
首先,由于它要使用到了LLM的SQL生成功能,需要通过复杂的提示来尽量提高LLM的生成准确度。
# 定义提示信息
query_gen_system = """You are a SQL expert with a strong attention to detail.
...
DO NOT make any DML statements (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, DROP etc.) to the database."""
# 定义提示模板
query_gen_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[("system", query_gen_system), ("placeholder", "{messages}")]
)
query_gen = query_gen_prompt | llm_chat_tongyi.bind_tools(
[SubmitFinalAnswer]
)如果这一步执行成功,我们希望LLM将最终完成的消息传递给END节点,所以这里我们也要告诉LLM最终完成消息的格式。因此,我们要给LLM绑定一个最终完成消息的格式。
# 定义最终完成消息的格式
class SubmitFinalAnswer(BaseModel):
"""Submit the final answer to the user based on the query results."""
final_answer: str = Field(..., description="The final answer to the user")
# 将提示模板和LLM集合起来,并绑定工具用于指定最终完成消息的格式
query_gen = query_gen_prompt | llm_chat_tongyi.bind_tools(
[SubmitFinalAnswer]
)LLM定义完成,接下来要定义节点的函数:
def query_gen_node(state: State):
message = query_gen.invoke(state)
# Sometimes, the LLM will hallucinate and call the wrong tool. We need to catch this and return an error message.
tool_messages = []
if message.tool_calls:
for tc in message.tool_calls:
if tc["name"] != "SubmitFinalAnswer":
tool_messages.append(
ToolMessage(
content=f"Error: The wrong tool was called: {tc['name']}. Please fix your mistakes. Remember to only call SubmitFinalAnswer to submit the final answer. Generated queries should be outputted WITHOUT a tool call.",
tool_call_id=tc["id"],
)
)
else:
tool_messages = []
return {"messages": [message] + tool_messages}这里通过的query_gen.invoke执行了LLM,然后对于返回的Message进行了解析。如果ToolMessage的tool_calls中包含了SubmitFinalAnswer的字样,意味着LLM判断输入是符合预期,可以作为最终答案提交的。反之则可能LLM产生了意料外的输出,这种情况下要抛出纠正消息,提示只能使用SubmitFinalAnswer作为回答。
然后将函数query_gen_node绑定给当前节点。
workflow.add_node("query_gen", query_gen_node)当前节点包含了决策路径,会产生分支处理。
# Define a conditional edge to decide whether to continue or end the workflow
def should_continue(state: State) -> Literal[END, "correct_query", "query_gen"]:
messages = state["messages"]
last_message = messages[-1]
# If there is a tool call, then we finish
if getattr(last_message, "tool_calls", None):
return END
if last_message.content.startswith("Error:"):
return "query_gen"
else:
return "correct_query"
# Specify the edges between the nodes
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"query_gen",
should_continue,
)从上面的代码可见,当前节点的输出Message中,有以下几种可能:
- Message中包含tool_call,并且是SubmitFinalAnswer。这种情况下,LLM判断下一步合适的做法是SubmitFinalAnswer,可以正常返回答案。
- Message中包含Error的字样。这种情况就是刚才处理的预期外输入,经过例外处理后Message被纠正为包含了Error字样的信息。这种情况下需要重新执行当前节点query_gen。
- Message中包含correct_query。这种情况意味着LLM判断下一步合适的做法是correct_query,并且没有指定tool_calls。这是符合正常处理的预期。
Node 6: correct_query
这个节点同样使用到了LLM。首先定义工具函数db_query_tool,这个函数尝试执行查询,如果失败了,就返回带有Error字样的字符串。
def db_query_tool(query: str) -> str:
"""
Execute a SQL query against the database and get back the result.
If the query is not correct, an error message will be returned.
If an error is returned, rewrite the query, check the query, and try again.
"""
result = db.run_no_throw(query)
if not result:
return "Error: Query failed. Please rewrite your query and try again."
return result接下来定义LLM的提示模板,并且将工具db_query_tool绑定给LLM。
query_check_system = """You are a SQL expert with a strong attention to detail.
Double check the SQLite ...
If there are any of the above mistakes, rewrite the query. If there are no mistakes, just reproduce the original query.
You will call the appropriate tool to execute the query after running this check."""
query_check_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[("system", query_check_system), ("placeholder", "{messages}")]
)
query_check = query_check_prompt | llm_chat_tongyi.bind_tools(
[db_query_tool], tool_choice="required"
)接下来,定义工具函数model_check_query,这个工具函数会执行LLM。
def model_check_query(state: State) -> dict[str, list[AIMessage]]:
"""
Use this tool to double-check if your query is correct before executing it.
"""
return {"messages": [query_check.invoke({"messages": [state["messages"][-1]]})]}最后将工具函数model_check_query绑定给节点。
# Add a node for the model to check the query before executing it
workflow.add_node("correct_query", model_check_query)在运行时,这个节点会使用LLM检查SQL。如果SQL看起来语法正确,那么LLM会返回AIMessage,内容包含如何调用db_query_tool来执行查询。
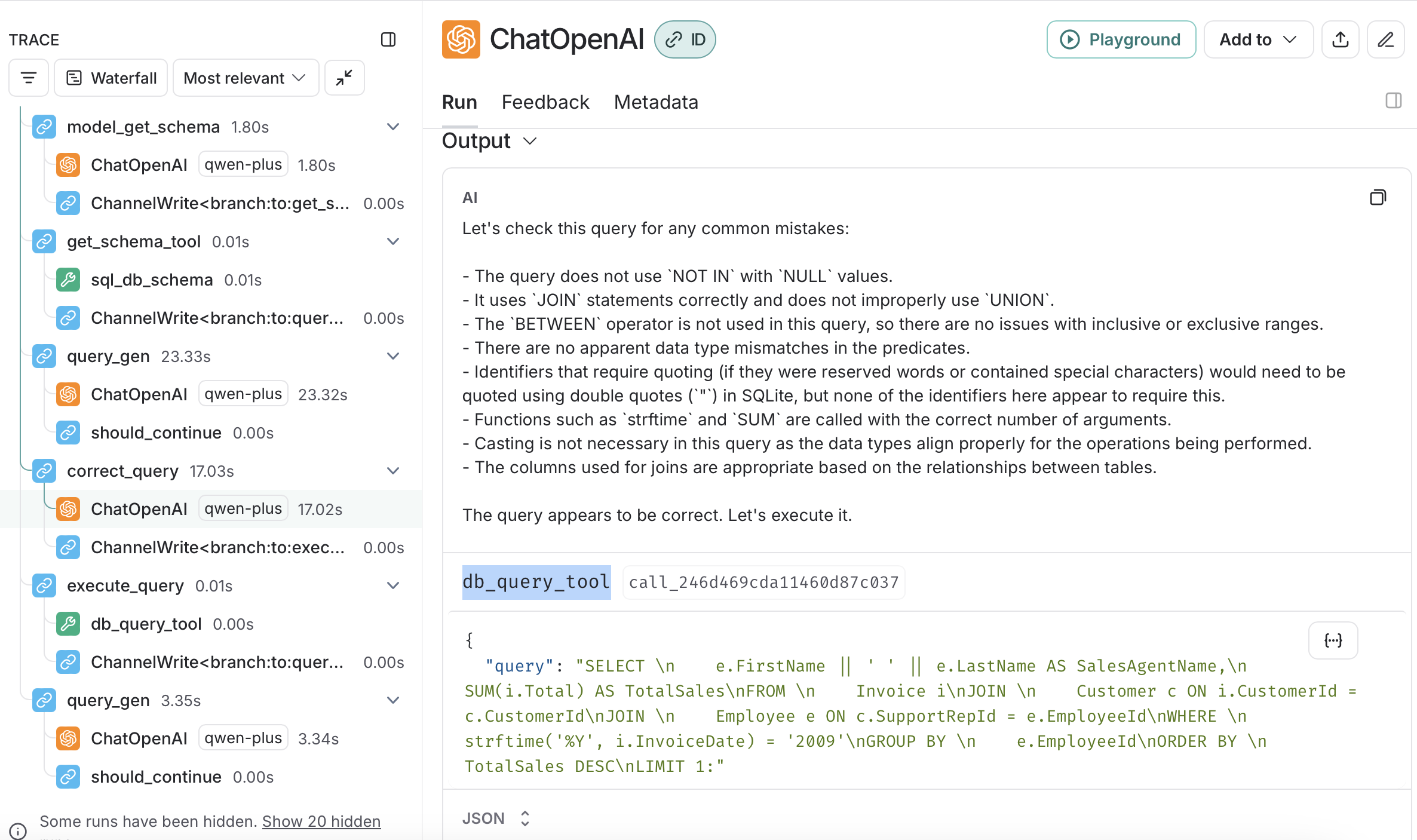
Node 7: execute_query
这个节点非常直观,直接将查询工具绑定到节点。
# Add node for executing the query
workflow.add_node("execute_query", create_tool_node_with_fallback([db_query_tool]))通过调用db_query_tool工具,可以将查询结果返回给工作流。
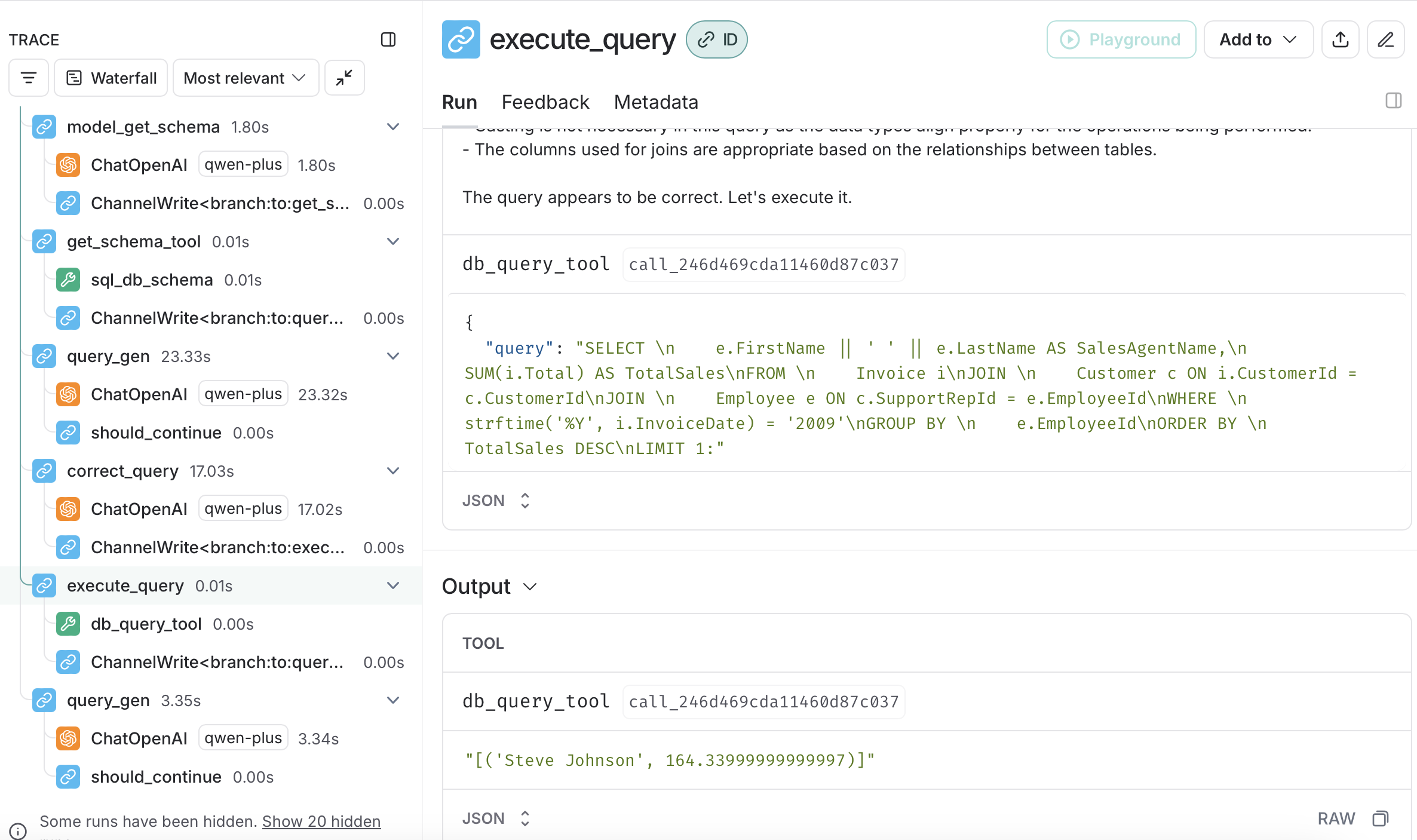
Node 8: END
结束处理
Summary
整个的智能体处理流程,结合了Langgraph的工具(主要是SQLDatabaseToolkit)和LLM,分别实现了具体数据库操作和决策支持。智能体工作流相比常规工作流,更加突出其中LLM的参与决策的特点。在执行的过程中,根据LLM的实际判断,会产生不同的处理分支。
由于不确定性的存在,在智能工作流中针对使用到LLM的节点,需要着重考虑各种意外的场景,结合强壮的fallback机制,确保智能体总是可以给出合理的最终处理结果。


